LGCH Todo System
LangGraph + Twilio + MCP + LangChain Voice AI agentic solution
Technical Architecture
System Architecture Overview
LGCH Todo System Architecture
Frontend Layer
Core Processing Layer
External Services Layer
Architecture Flow: Multi-layered system with voice/web interfaces, AI processing, and external service integration for comprehensive productivity management.
Overview
The LGCH Todo System leverages the power of LangGraph, Model Context Protocol (MCP), and LangChain to create an intelligent voice-enabled AI assistant named Luna.
This system demonstrates advanced agent architecture with tool-calling capabilities, state management, and seamless integration with external services.
Luna can manage to-do tasks, reminders, and calendar events through natural voice interactions or web API calls.
All data is stored in a PostgreSQL database and automatically synchronized with Google Calendar,
providing a comprehensive productivity management solution.
Core Technologies
- • LangGraph for agent orchestration
- • Model Context Protocol (MCP) for tool management
- • LangChain for LLM integration
- • Flask for web API endpoints
- • SQLAlchemy for database operations
- • OpenAI APIs (GPT-4, Whisper, TTS)
- • Twilio for phone integration
- • ngrok for secure tunneling
- • WebSocket for real-time communication
Key Features
- • Voice-enabled AI assistant (Luna)
- • Todo list management with priorities
- • Reminder system with importance levels
- • Calendar event management
- • Google Calendar integration
- • RESTful API endpoints
- • Real-time voice interaction
- • Twilio phone integration
- • ngrok tunnel management
- • WebSocket real-time communication
Module Structure
LGCH Todo System Structure
Project Root/
├── app.py # Main Flask application
├── start_servers.py # Production server startup script
├── setup_ngrok_tunnels.py # ngrok tunnel management
├── ngrok.yml # ngrok configuration file
├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
├── recordings/ # Call recording storage (git-ignored)
└── lgch_todo/ # LGCH Todo module
├── __init__.py # Package initialization, exports blueprint
├── routes.py # Flask routes and Twilio webhooks
├── http_websocket_server.py # Hybrid HTTP/WebSocket server
├── twilio_handler.py # Twilio Media Streams handler
├── assistant_graph_todo.py # LangGraph agent definition
├── state.py # Agent state management
├── voice_utils.py # Audio recording and playback
├── templates/ # Flask templates
│ └── lgch_todo_index.html
└── mcps/ # Model Context Protocol servers
├── mcp_config.json # MCP server configuration
└── local_servers/
├── db_todo.py # Database operations via MCP
└── google_calendar.py # Calendar operations via MCP
LangGraph Agent Architecture
LangGraph Workflow Diagram
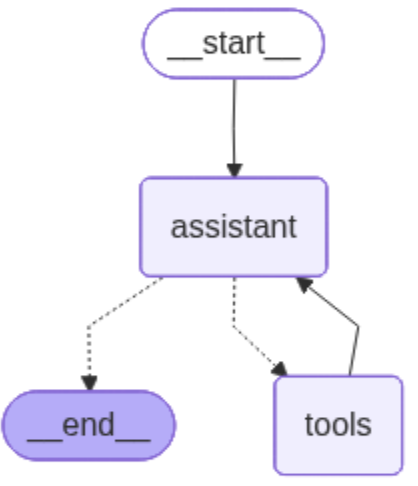
LangGraph Workflow: The agent can either continue to use tools or end the conversation based on user input and context.
Agent Components
- • TodoAgent Class: Main agent orchestrator
- • StateGraph: Manages conversation flow
- • Assistant Node: LLM reasoning and response generation
- • Tool Node: Executes MCP tools
- • Conditional Edges: Routes between nodes based on tool calls
State Management
- • AgentState: Conversation state with message history
- • Message History: Maintains conversation context
- • Customer ID: User identification
- • Checkpointer: InMemorySaver for state persistence
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Integration
MCP provides a standardized way for AI agents to interact with external tools and services. The LGCH system uses MCP to expose database operations and Google Calendar integration as tools.
MCP Tool Integration Flow
Agent
Client
Server
MCP Flow: LangGraph agent communicates with MCP client, which manages multiple MCP servers for database and calendar operations.
MCP Server Configuration
{
"mcpServers": {
"db": {
"command": "python",
"args": ["./mcps/local_servers/db_todo.py"],
"transport": "stdio"
}
}
}
Available Tools
- • create_todo - Create new todo items
- • get_todos - Retrieve all todos
- • complete_todo - Mark todos as completed
- • update_todo - Modify todo properties
- • delete_todo - Remove todo items
- • create_reminder - Add new reminders
- • get_reminders - List all reminders
- • delete_reminder - Remove reminders
- • create_calendar_event - Schedule events
- • get_calendar_events - List calendar events
- • delete_calendar_event - Remove events
- • query_db - Execute custom SQL queries
Data Layer (MCP Server)
Todo Model
- • id: UUID primary key
- • title: Task title
- • description: Optional details
- • completed: Boolean status
- • priority: low/medium/high/urgent
- • due_date: Optional deadline
- • google_calendar_event_id
Reminder Model
- • id: UUID primary key
- • reminder_text: Reminder content
- • importance: low/medium/high/urgent
- • reminder_date: Optional date/time
- • google_calendar_event_id
CalendarEvent Model
- • id: UUID primary key
- • title: Event title
- • description: Event details
- • event_from: Start datetime
- • event_to: End datetime
- • google_calendar_event_id
Enhanced LangGraph Tool Calls
The LangGraph implementation provides intelligent tool calling capabilities with dynamic tool selection and error handling. The agent automatically chooses appropriate tools based on user intent and maintains conversation context for seamless interactions.
Tool Calls Flow Diagram
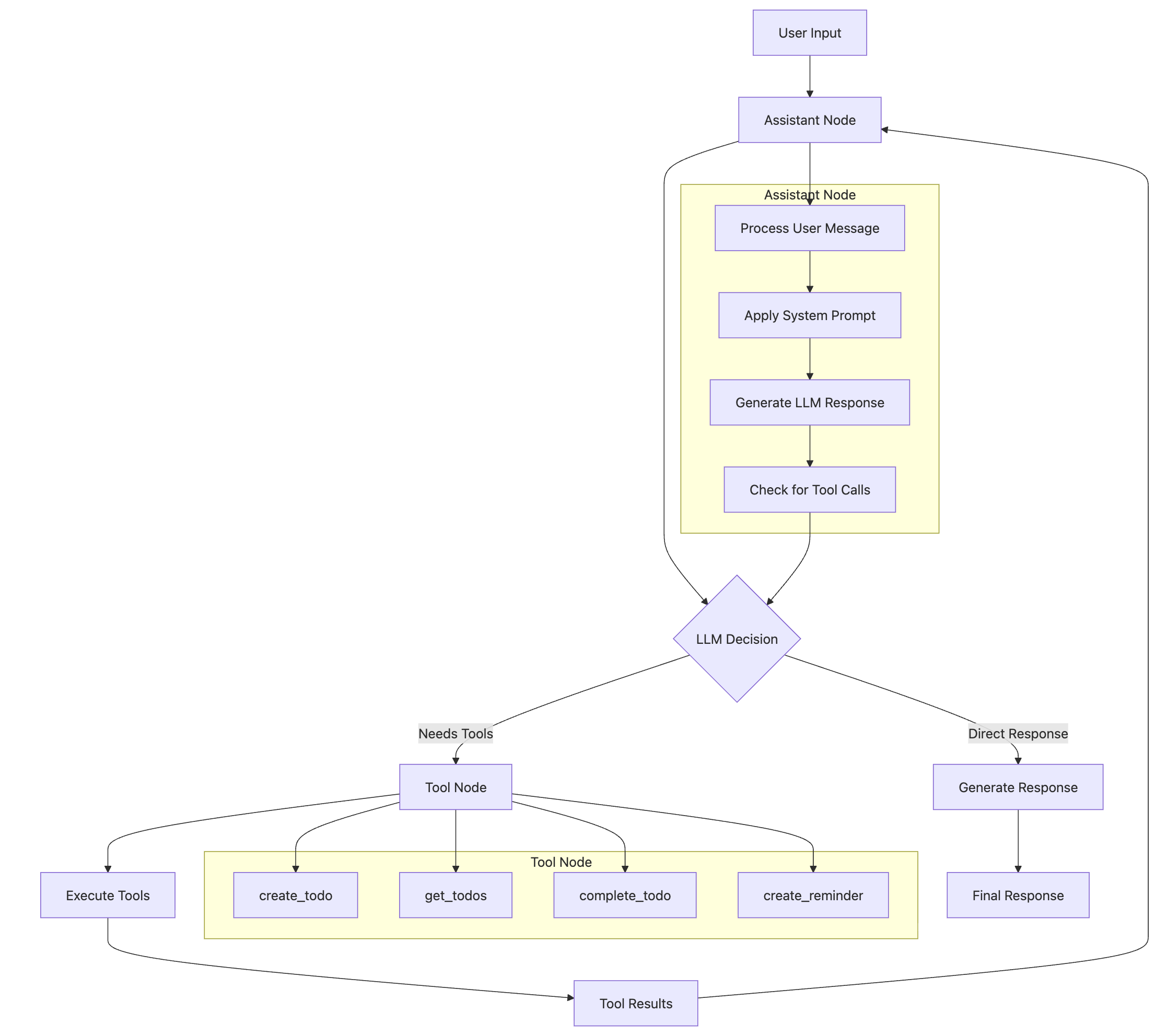
Tool Calls Flow: LangGraph implementation showing dynamic tool selection and intelligent orchestration of MCP tools.
Tool Calls Features
MCP Integration
- • Database operations via MCP servers
- • Google Calendar synchronization
- • Real-time tool discovery
- • Secure tool communication
Error Handling
- • Graceful tool failure recovery
- • Timeout management
- • Fallback strategies
- • User-friendly error messages
Tool Features: Intelligent tool calling system with error recovery and seamless MCP integration.
Core Tool Calling Capabilities
- • Dynamic Tool Selection: LLM intelligently chooses appropriate tools based on user intent
- • Error Recovery: Graceful handling of tool failures with fallback strategies
- • Context Awareness: Tools access conversation history and maintain state
- • Streaming Responses: Real-time tool execution updates for better user experience
API Endpoints
Web Interface
GET /- Main portfolio pageGET /lgch_todo/- LGCH Todo web interfaceGET /lgch-tech-spec- Technical specification
Agent API
POST /lgch_todo/run_agent- Run Luna agentWS localhost:5001- WebSocket server (separate process)
Request Format:
{
"prompt": "Create a high priority todo"
}Twilio Integration
POST /lgch_todo/twilio/call- Handle incoming callsPOST /lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio- Process speech inputWS localhost:5001- Real-time audio streaming
TwiML Response:
<Response>
<Say voice="Polly.Amy">Hello! I'm Luna...</Say>
<Gather input="speech"
action="/lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio">
</Gather>
</Response>Voice Interface
Luna provides a complete voice interface using OpenAI's Whisper for speech-to-text and TTS for text-to-speech responses. The system supports both local voice interaction and phone-based voice calls through Twilio integration.
Voice Processing Pipeline
Voice Pipeline: Complete end-to-end voice processing from audio input to AI-generated speech output with real-time streaming capabilities.
Voice Components
- • Speech-to-Text: OpenAI Whisper API
- • Text-to-Speech: OpenAI TTS API (gpt-4o-mini-tts)
- • Audio Processing: sounddevice & scipy libraries
- • Audio Format: μ-law to PCM conversion
- • Voice Model: fable voice with cheerful tone
- • Streaming: Real-time audio chunk processing
Processing Flow
- 1. Audio received via WebSocket
- 2. Base64 decoded to audio buffer
- 3. μ-law converted to PCM for Whisper
- 4. Speech transcribed via Whisper API
- 5. Text processed by LangGraph agent
- 6. Response generated with MCP tools
- 7. Text converted to speech via TTS
- 8. Audio streamed back via WebSocket
Twilio Phone Integration
Luna can be accessed via phone calls through Twilio integration, allowing users to interact with the AI assistant through voice calls from any phone number. The system uses a sophisticated WebSocket-based architecture for real-time voice processing.
Twilio Call Flow Architecture
Call Flow: Twilio Call → WebSocket → http_websocket_server.py → twilio_handler.py → voice_utils.py → assistant_graph_todo.py
Twilio Components
- • Twilio Voice API: Handles incoming/outgoing calls
- • Media Streams: Real-time audio streaming
- • Webhook Endpoints: Flask routes for call handling
- • TwiML Responses: Call flow instructions
- • WebSocket Bridge: Bidirectional audio streaming
- • ngrok Tunneling: Secure public access
Call Flow Process
- 1. User calls Twilio phone number
- 2. Twilio webhook triggers Flask endpoint
- 3. TwiML response starts Media Stream
- 4. WebSocket connection to port 5001
- 5. Audio streamed to twilio_handler.py
- 6. Speech processed via voice_utils.py
- 7. LangGraph agent generates response
- 8. Audio streamed back to caller
Twilio Configuration
# Environment Variables
TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID=your_account_sid
TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN=your_auth_token
TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER=+1234567890
WEBHOOK_BASE_URL=https://your-ngrok-url.ngrok.io
# Webhook Endpoints
POST /lgch_todo/twilio/call - Handle incoming calls
POST /lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio - Process speech input
WS localhost:5001 - WebSocket server (separate process)
# TwiML Response
<Response>
<Gather action="/lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio" method="POST" input="speech" speechTimeout="auto" timeout="10" barge_in="true">
<Say voice="Polly.Amy">Hello! I'm Luna...</Say>
</Gather>
<Say voice="Polly.Amy">I didn't hear anything. Please try again.</Say>
<Redirect>/lgch_todo/twilio/call?is_continuation=true</Redirect>
</Response>
ngrok Tunnel Configuration
ngrok provides secure tunneling to expose local development servers to the internet, enabling Twilio webhooks and external API access. The system includes automated ngrok management for seamless development and deployment.
ngrok Tunnel Architecture
Local Development
ngrok Tunnels
External Access
Tunnel Flow: ngrok creates secure tunnels from local development servers to public URLs, enabling external service integration.
ngrok Features
- • Automatic Tunnel Management: Start/stop tunnels programmatically
- • HTTP Tunnel Support: Flask (5000) and WebSocket (5001) via HTTP
- • HTTPS/WSS Support: Automatic SSL/TLS for secure connections
- • Real-time Monitoring: Tunnel status via ngrok API (port 4040)
- • Configuration Management: YAML-based setup with ngrok.yml
- • Process Management: Automated tunnel lifecycle management
Tunnel Setup
# ngrok.yml configuration
version: "2"
authtoken: your_ngrok_token
tunnels:
flask:
proto: http
addr: 5000
schemes: [https]
websocket:
proto: http
addr: 5001
schemes: [https]
Automated Tunnel Management
# Python script for tunnel management (setup_ngrok_tunnels.py)
import subprocess
import requests
import time
import sys
import os
def get_ngrok_tunnels():
"""Get active ngrok tunnels from API."""
try:
response = requests.get("http://localhost:4040/api/tunnels", timeout=5)
return response.json()
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ Could not connect to ngrok API: {e}")
return None
def create_ngrok_tunnel(port, name, protocol="http"):
"""Create an ngrok tunnel for a specific port."""
print(f"🔗 Creating ngrok tunnel for {name} on port {port}...")
# Kill any existing tunnels on this port
subprocess.run(["pkill", "-f", f"ngrok.*{port}"], check=False)
time.sleep(2)
# Start ngrok tunnel
cmd = ["ngrok", "http", str(port), "--log=stdout"]
process = subprocess.Popen(cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
# Wait for tunnel to be ready
print(f"⏳ Waiting for {name} tunnel to initialize...")
time.sleep(5)
# Get tunnel info with retries
for attempt in range(3):
tunnels = get_ngrok_tunnels()
if tunnels and 'tunnels' in tunnels:
for tunnel in tunnels['tunnels']:
addr = tunnel['config']['addr']
if (addr == f'localhost:{port}' or
addr == f'127.0.0.1:{port}'):
public_url = tunnel['public_url']
print(f"✅ {name} tunnel created: {public_url}")
return public_url, process
if attempt < 2:
print(f"⏳ Retrying tunnel detection for {name}...")
time.sleep(2)
print(f"❌ Failed to create {name} tunnel")
process.terminate()
return None, None
def main():
print("🚀 Setting up ngrok tunnels for Twilio integration...")
# Create tunnels
flask_url, flask_process = create_ngrok_tunnel(5000, "Flask Server", "http")
websocket_url, websocket_process = create_ngrok_tunnel(5001, "WebSocket Server", "http")
if flask_url:
print(f"📞 Flask Server: {flask_url}")
if websocket_url:
print(f"🔌 WebSocket Server: {websocket_url}")
print(f"📱 Twilio Webhook URL: {flask_url}/lgch_todo/twilio/call")
try:
# Keep running
while True:
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("🛑 Stopping ngrok tunnels...")
if flask_process:
flask_process.terminate()
if websocket_process:
websocket_process.terminate()
print("✅ Tunnels stopped.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Code Examples
LangGraph Agent (assistant_graph_todo.py)
from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
class TodoAgent:
def __init__(self, tools: List[BaseTool] = []):
self.tools = tools
self.llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4.1-mini-2025-04-14").bind_tools(tools=self.tools)
self.graph = self.build_graph()
def build_graph(self) -> CompiledStateGraph:
builder = StateGraph(AgentState)
def assistant(state: AgentState):
response = self.llm.invoke(state.messages)
state.messages.append(response)
return state
builder.add_node("assistant", assistant)
builder.add_node("tools", ToolNode(self.tools))
builder.set_entry_point("assistant")
builder.add_conditional_edges("assistant", tools_condition)
builder.add_edge("tools", "assistant")
return builder.compile(checkpointer=InMemorySaver())Flask API Routes (routes.py)
from flask import Blueprint, request, jsonify, render_template, Response
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
import asyncio
import json
import os
import requests
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
from .assistant_graph_todo import TodoAgent
from .state import AgentState
lgch_todo_bp = Blueprint('lgch_todo', __name__, url_prefix='/lgch_todo')
@lgch_todo_bp.route('/')
def index():
"""Web interface endpoint."""
template_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'templates', 'lgch_todo_index.html')
if os.path.exists(template_path):
return render_template('lgch_todo_index.html')
return "LGCH Todo: LangGraph + MCP integration is ready. POST to /lgch_todo/run_agent with JSON {prompt: str}."
async def _get_agent_graph() -> StateGraph:
"""Helper to initialize the agent graph with tools."""
config_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'mcps', 'mcp_config.json')
if not os.path.exists(config_path):
# Fallback path for when running from the root directory
config_path = os.path.join('lgch_todo', 'mcps', 'mcp_config.json')
with open(config_path) as f:
mcp_config = json.load(f)
# Set working directory to project root for MCP servers
project_root = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__))
original_cwd = os.getcwd()
os.chdir(project_root)
# Update the MCP config with absolute paths
for server_name, server_config in mcp_config["mcpServers"].items():
if "args" in server_config and len(server_config["args"]) > 0:
relative_path = server_config["args"][0]
if not os.path.isabs(relative_path):
absolute_path = os.path.join(project_root, relative_path)
server_config["args"][0] = absolute_path
try:
client = MultiServerMCPClient(connections=mcp_config["mcpServers"])
tools = await client.get_tools()
return TodoAgent(tools=tools).build_graph()
finally:
os.chdir(original_cwd)
async def _run_agent_async(prompt: str) -> str:
"""Runs the agent for a given prompt and returns the final response."""
agent_graph = await _get_agent_graph()
input_state = AgentState(
messages=[HumanMessage(content=prompt)],
customer_id=""
)
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "flask-thread-1"}}
# Stream through the graph to execute the agent logic
async for _ in agent_graph.astream(input=input_state, stream_mode="values", config=config):
pass
final_state = agent_graph.get_state(config=config)
last_message = final_state.values.get("messages")[-1]
return getattr(last_message, 'content', "")
@lgch_todo_bp.route('/run_agent', methods=['POST'])
def run_agent():
"""API endpoint for running the agent with a text prompt."""
data = request.get_json(silent=True) or {}
prompt = data.get('prompt')
if not prompt:
return jsonify({"error": "Missing 'prompt' in JSON body"}), 400
try:
result = asyncio.run(_run_agent_async(prompt))
return jsonify({"result": result})
except Exception as e:
# Log the full error for debugging
print(f"Error in /run_agent: {e}")
return jsonify({"error": str(e)}), 500MCP Server Tools (db_todo.py)
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
from sqlalchemy.orm import Session
from .models import DBTodo, DBReminder, DBCalendarEvent
mcp = FastMCP("db_todo")
@mcp.tool()
async def create_todo(
title: str,
description: Optional[str] = None,
priority: TodoPriority = TodoPriority.MEDIUM,
due_date: Optional[datetime] = None,
) -> str:
"""Create a new todo item with title, description, priority, and optional due date."""
with SessionLocal() as session:
new_todo = DBTodo(
title=title,
description=description,
priority=priority.value,
due_date=due_date,
)
session.add(new_todo)
session.commit()
session.refresh(new_todo)
# Sync with Google Calendar
try:
calendar_service = get_calendar_service()
google_event_id = calendar_service.create_event(
title=f"TODO: {title}",
description=description or "Task from LGCH Todo System"
)
if google_event_id:
new_todo.google_calendar_event_id = google_event_id
session.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to sync with Google Calendar: {e}")
return Todo.model_validate(new_todo.__dict__).model_dump_json(indent=2)Voice Interface (voice_utils.py)
import sounddevice as sd
import scipy.io.wavfile as wav
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
async def record_audio_until_stop() -> str:
"""Record audio from microphone until Enter is pressed."""
print("Recording... Press Enter to stop.")
# Record audio
sample_rate = 44100
audio_data = sd.rec(int(sample_rate * 60), samplerate=sample_rate, channels=1)
input("Press Enter to stop recording...")
sd.stop()
# Save and transcribe
wav.write("temp_audio.wav", sample_rate, audio_data)
with open("temp_audio.wav", "rb") as audio_file:
transcript = await openai_async.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-1",
file=audio_file
)
return transcript.text
async def play_audio(message: str):
"""Convert text to speech and play audio."""
response = await openai_async.audio.speech.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini-tts",
voice="fable",
input=message,
instructions="Speak in a cheerful, helpful tone with a brisk pace.",
response_format="pcm",
speed=1.2,
)
# Play audio using sounddevice
audio_data = np.frombuffer(response.content, dtype=np.int16)
sd.play(audio_data, samplerate=24000)
sd.wait()Twilio Webhook Handler (routes.py)
from flask import Blueprint, request, Response
from twilio.twiml.voice_response import VoiceResponse, Gather
import asyncio
import json
import os
import requests
lgch_todo_bp = Blueprint('lgch_todo', __name__, url_prefix='/lgch_todo')
def get_webhook_base_url():
"""Get the webhook base URL for Twilio webhooks."""
if os.getenv('FLASK_ENV') == 'production':
return os.getenv('WEBHOOK_BASE_URL', 'https://hjlees.com')
else:
# Development: Try ngrok first, fallback to localhost
try:
response = requests.get("http://localhost:4040/api/tunnels", timeout=5)
tunnels = response.json()
for tunnel in tunnels.get('tunnels', []):
if tunnel.get('config', {}).get('addr') == 'http://localhost:5000':
return tunnel.get('public_url', 'http://localhost:5000')
return "http://localhost:5000"
except Exception:
return "http://localhost:5000"
@lgch_todo_bp.route('/twilio/call', methods=['POST'])
def twilio_call_webhook():
"""Handles incoming calls from Twilio with barge-in capability."""
is_continuation = request.args.get('is_continuation', 'false').lower() == 'true'
response = VoiceResponse()
# Use Gather to collect speech input with barge-in capability
gather = response.gather(
input='speech',
action='/lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio',
method='POST',
speech_timeout='auto',
timeout=10,
barge_in=True # Enable barge-in to interrupt while speaking
)
# Only say the welcome message if this is the initial call
if not is_continuation:
gather.say("Hello! I'm Luna, your personal productivity assistant. How can I help you today?", voice='Polly.Amy')
# Fallback if no speech is detected
response.say("I didn't hear anything. Please try again.", voice='Polly.Amy')
response.redirect('/lgch_todo/twilio/call?is_continuation=true')
return Response(str(response), mimetype='text/xml')
@lgch_todo_bp.route('/twilio/process_audio', methods=['POST'])
def process_audio_webhook():
"""Handles audio processing requests from Twilio."""
try:
transcribed_text = request.form.get('SpeechResult', '')
call_sid = request.form.get('CallSid', '')
if not transcribed_text or len(transcribed_text.strip()) < 2:
response = VoiceResponse()
gather = Gather(
input='speech',
action='/lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio',
method='POST',
speech_timeout='auto',
timeout=10,
barge_in=True
)
gather.say("I didn't catch that. Could you please repeat?", voice='Polly.Amy')
response.append(gather)
response.say("I didn't hear anything. Please try again.", voice='Polly.Amy')
response.redirect('/lgch_todo/twilio/call?is_continuation=true')
return Response(str(response), mimetype='text/xml')
# Check if user wants to end the call
exit_phrases = ['exit', 'goodbye', 'bye', 'that\'s it', 'thank you', 'done']
if any(phrase in transcribed_text.lower() for phrase in exit_phrases):
response = VoiceResponse()
response.say("Thank you for using Luna! Have a great day!", voice='Polly.Amy')
response.hangup()
return Response(str(response), mimetype='text/xml')
# Process with the agent
agent_response = asyncio.run(_run_agent_async(transcribed_text))
# Return TwiML with the agent's response and barge-in capability
response = VoiceResponse()
gather = Gather(
input='speech',
action='/lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio',
method='POST',
speech_timeout='auto',
timeout=10,
barge_in=True # Enable barge-in to interrupt while speaking
)
gather.say(agent_response, voice='Polly.Amy')
response.append(gather)
response.say("I didn't hear anything. Please try again.", voice='Polly.Amy')
response.redirect('/lgch_todo/twilio/call?is_continuation=true')
return Response(str(response), mimetype='text/xml')
except Exception as e:
response = VoiceResponse()
gather = Gather(
input='speech',
action='/lgch_todo/twilio/process_audio',
method='POST',
speech_timeout='auto',
timeout=10,
barge_in=True
)
gather.say("I'm sorry, I encountered an error. Please try again.", voice='Polly.Amy')
response.append(gather)
response.say("I didn't hear anything. Please try again.", voice='Polly.Amy')
response.redirect('/lgch_todo/twilio/call?is_continuation=true')
return Response(str(response), mimetype='text/xml')Usage Guide
Setup and Deployment
1. Environment Setup
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Set up environment variables
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your_openai_key"
export TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID="your_twilio_sid"
export TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN="your_twilio_token"
export TWILIO_PHONE_NUMBER="+1234567890"
export GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS_FILE="path/to/credentials.json"
export DB_URI="postgresql://user:pass@localhost/lgch_todo"2. ngrok Configuration
# Install ngrok
brew install ngrok # macOS
# or download from https://ngrok.com/
# Configure ngrok
ngrok config add-authtoken your_ngrok_token
# Start tunnels
python setup_ngrok_tunnels.py3. Twilio Setup
Step 1: Configure Voice Settings
In your Twilio Console, navigate to Phone Numbers → Manage → Active numbers and select your phone number.
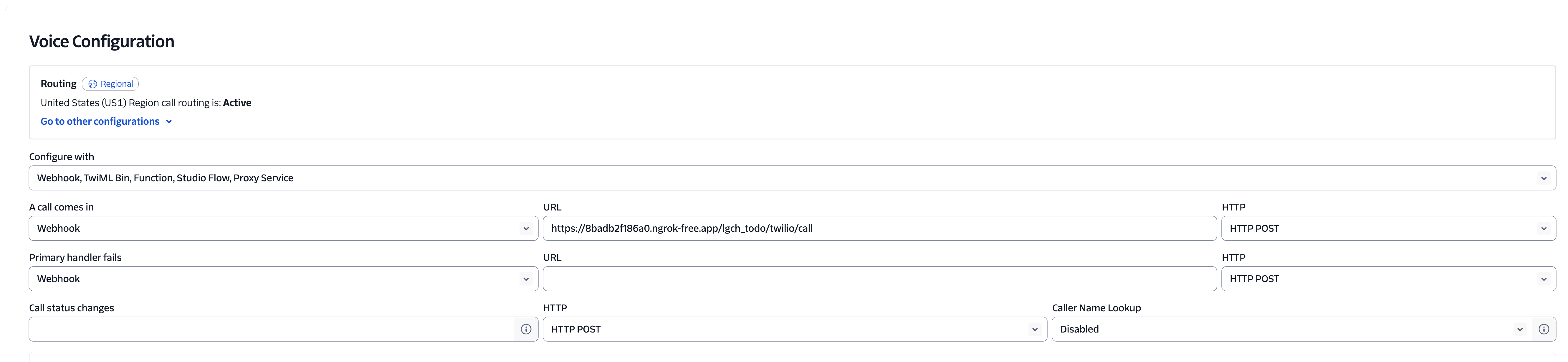
Configure the voice settings as shown above, ensuring the webhook URL points to your ngrok tunnel.
Step 2: Set Webhook URL
Update your Twilio phone number webhook to point to your ngrok tunnel:
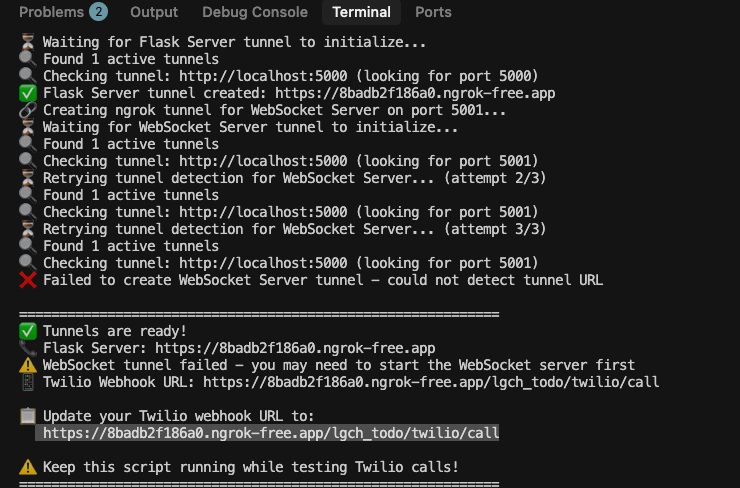
# Webhook URL format:
https://your-ngrok-url.ngrok.io/lgch_todo/twilio/call
# Example like screenshot:
https://8badb2f186a0.ngrok-free.app/lgch_todo/twilio/callStep 3: Test Integration
# Test the webhook endpoint
curl -X POST https://your-ngrok-url.ngrok.io/lgch_todo/twilio/call \
-d "CallSid=test123&From=+1234567890"
# Expected response: TwiML with Luna's greeting4. Start Production Services
# Terminal 1: Start application servers
python start_servers.py
# Terminal 2: Start ngrok tunnels for Twilio integration
python setup_ngrok_tunnels.py
# Verify services are running:
# - Flask Server: http://localhost:5000
# - WebSocket Server: ws://localhost:5001
# - ngrok Tunnels: Check ngrok dashboard at http://localhost:40405. Production Verification
# Test Twilio webhook endpoint
curl -X POST https://your-ngrok-url.ngrok.io/lgch_todo/twilio/call \
-d "CallSid=test123&From=+1234567890"
# Check service health
curl http://localhost:5000/lgch_todo/run_agent \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"prompt": "Test connection"}'
# Monitor logs for any errors
tail -f logs/app.log # if logging is configuredProduction Usage
Phone Integration via Twilio
Once deployed, users can call your Twilio phone number to interact with Luna. The system supports barge-in functionality, allowing users to interrupt the agent while speaking.
Note: Ensure your Twilio webhook URL is properly configured to point to your ngrok tunnel URL.
Todo Management
- • "Create a high priority todo to buy groceries"
- • "Show me all my pending todos"
- • "Mark the grocery shopping todo as completed"
- • "Update the project todo with a new description"
- • "Delete the old todo about cleaning"
Reminders & Calendar
- • "Create a reminder to call mom tomorrow at 2 PM"
- • "Schedule a meeting for next Friday from 2 to 3 PM"
- • "What's on my calendar for this week?"
- • "Add a reminder about the dentist appointment"
- • "Show me all my upcoming events"
Test Result and Validation
The LGCH Todo system has been thoroughly tested with a focus on the core MCP tools: create_todo, complete_todo, create_reminder, and delete_reminder functionality. All tests demonstrate successful integration across voice interface, database operations, and Google Calendar synchronization.
1. Create Todo Tool
Comprehensive testing of the create_todo MCP tool across all integration points, demonstrating end-to-end functionality from voice input to database storage and calendar synchronization.
Voice Interface
Voice-to-text transcription and todo creation through the create_todo MCP tool.
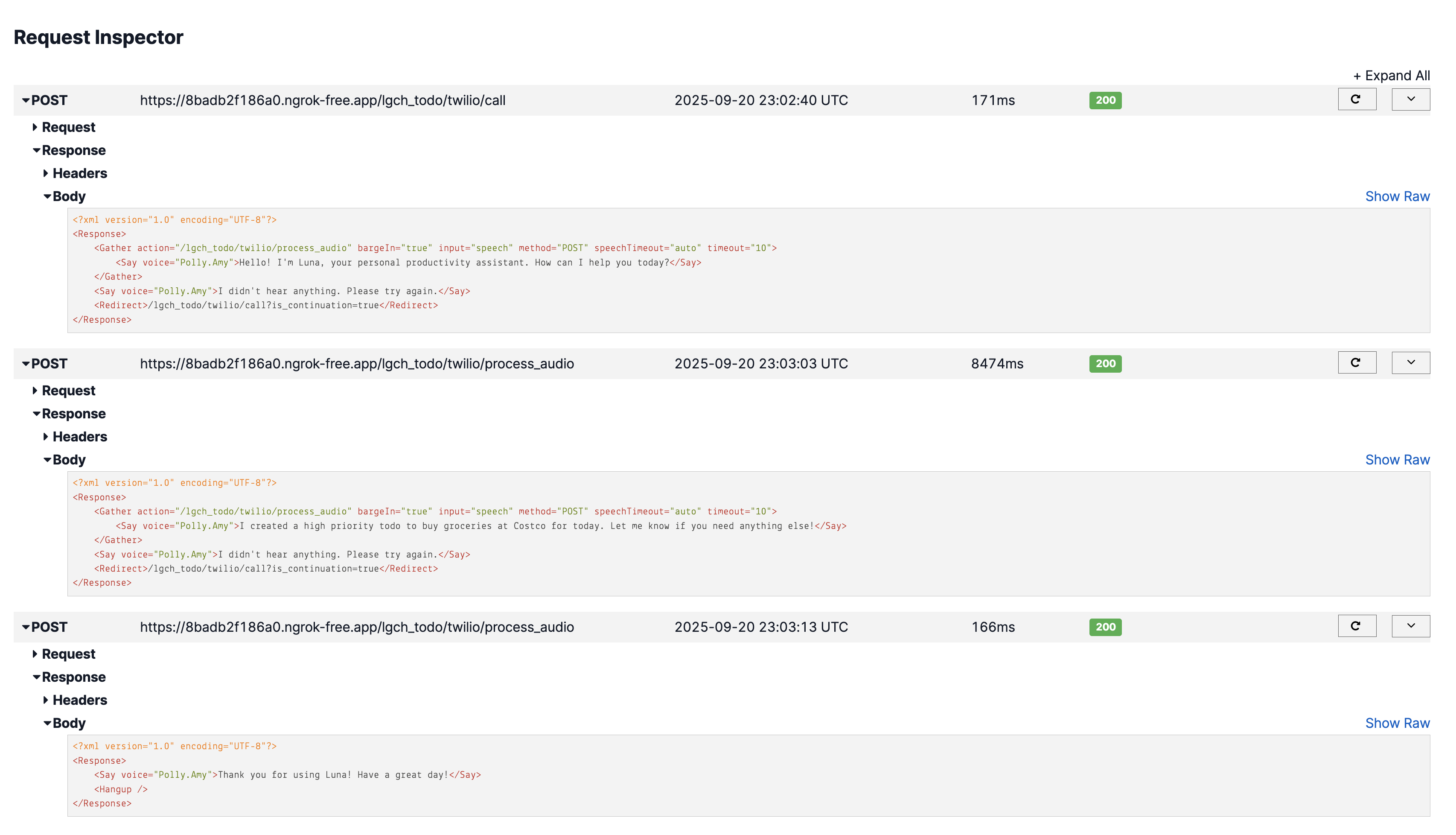
Audio: "Create a high priority todo task to buy groceries at Costco"
Output: ✅ Todo created via voice
Database Storage
create_todo MCP tool successfully stores todos in PostgreSQL database.
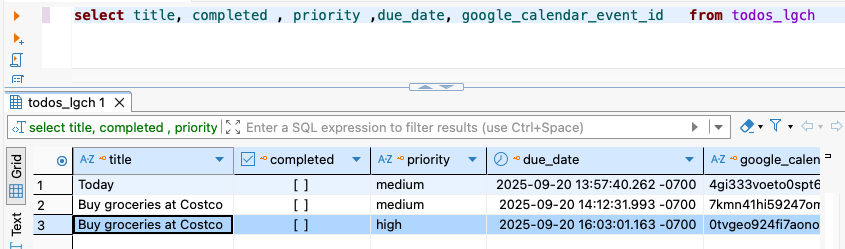
Result: ✅ Todo persisted in DB
Calendar Synchronization
create_todo tool automatically syncs todos to Google Calendar events.
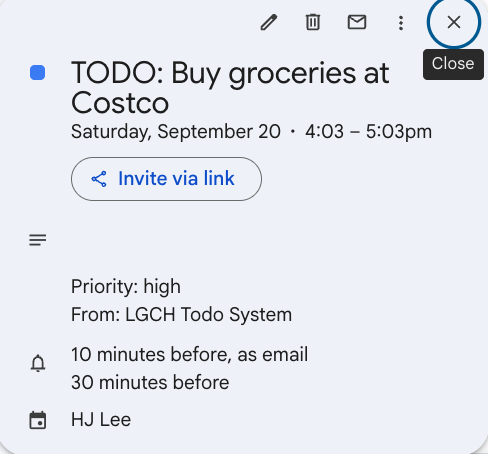
Result: ✅ Event created in Google Calendar
2. Complete Todo Tool
Comprehensive testing of the complete_todo MCP tool functionality, demonstrating successful todo completion workflow from voice input to database update and calendar synchronization.
Voice Interface
Voice-to-text transcription and todo completion through the complete_todo MCP tool.
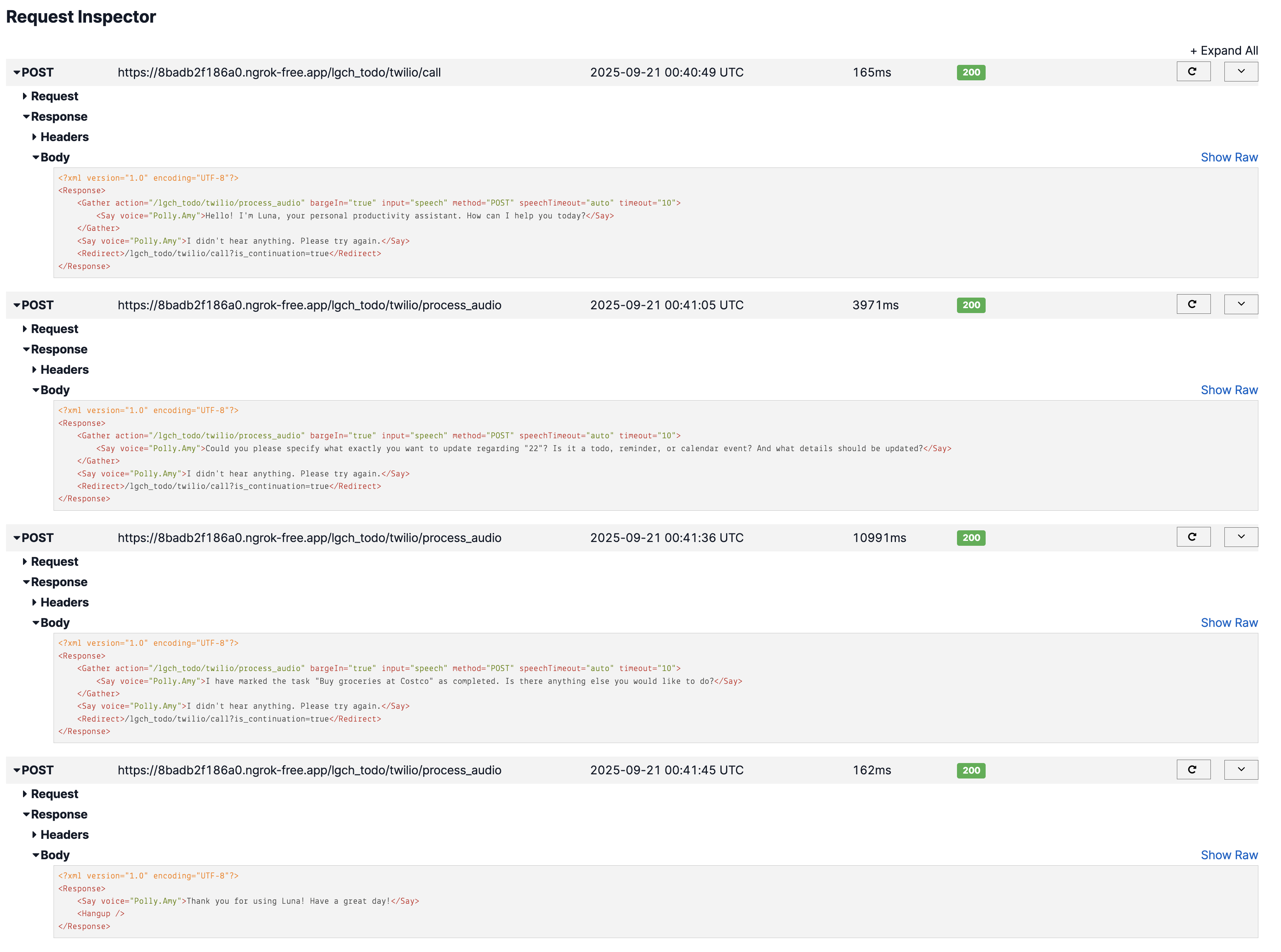
Audio: "Buy groceries at Costco needs to completed"
Output: ✅ Todo marked as completed via voice
Database Update
complete_todo MCP tool successfully updates todo status in PostgreSQL database.
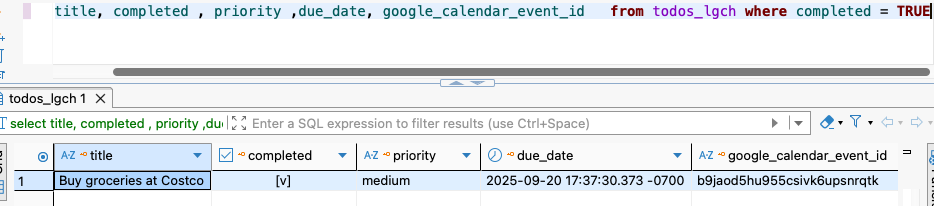
Result: ✅ Todo status updated to completed
Calendar Synchronization
complete_todo tool automatically updates corresponding Google Calendar event.
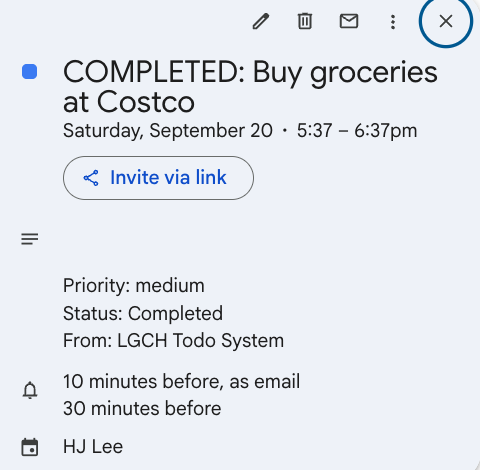
Result: ✅ Calendar event marked as completed
3. Create Reminder Tool
Comprehensive testing of the create_reminder MCP tool functionality, demonstrating successful reminder creation workflow from voice input to database storage and calendar synchronization.
Voice Interface
Voice-to-text transcription and reminder creation through the create_reminder MCP tool.
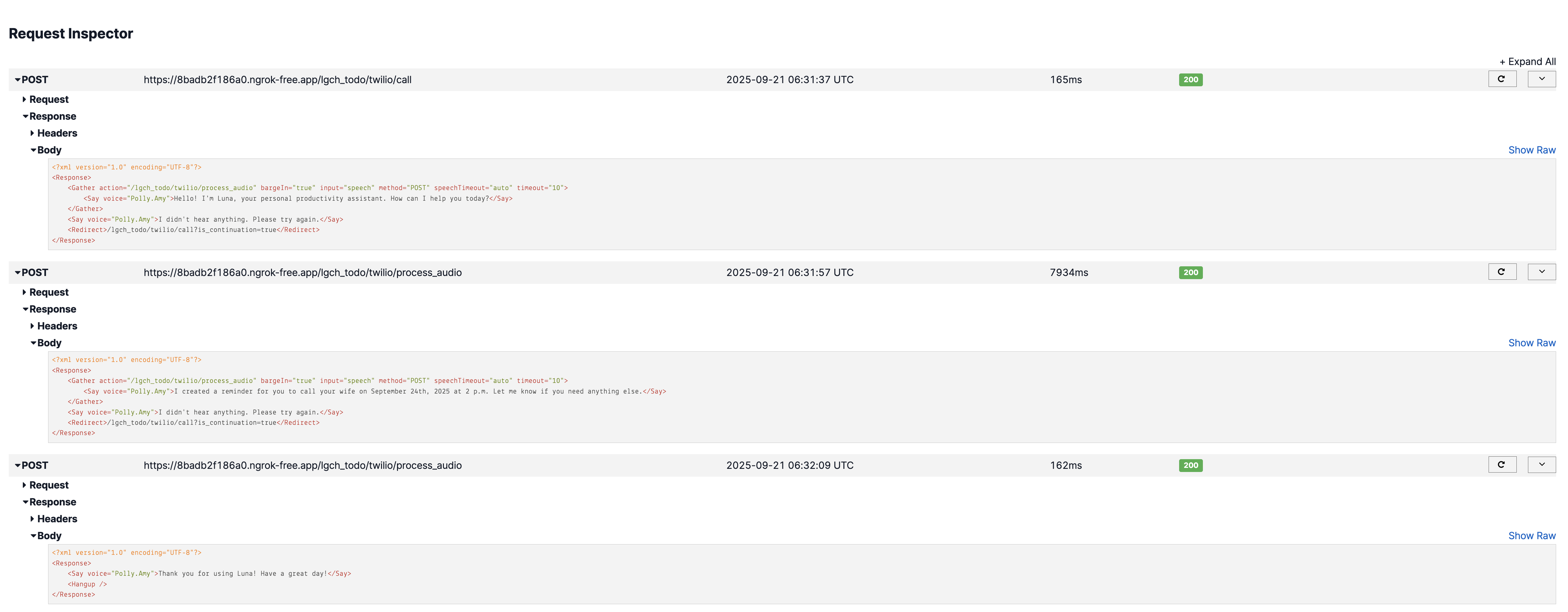
Audio: "Create a reminder to call my wife ~~~~ at 2 PM"
Output: ✅ Reminder created via voice
Database Storage
create_reminder MCP tool successfully stores reminders in PostgreSQL database.
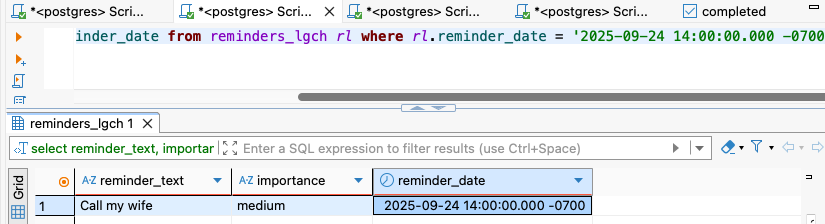
Result: ✅ Reminder persisted in DB
Calendar Synchronization
create_reminder tool automatically syncs reminders to Google Calendar events.
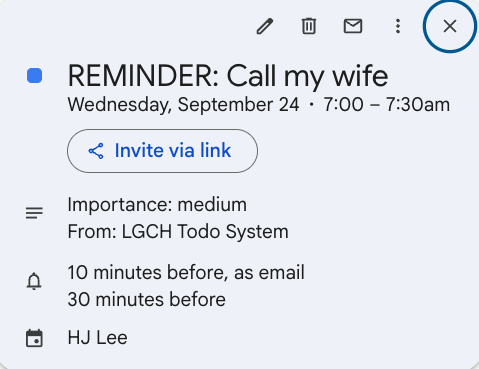
Result: ✅ Event created in Google Calendar
4. Delete Reminder Tool
Comprehensive testing of the delete_reminder MCP tool functionality, demonstrating successful reminder deletion workflow from voice input to database removal and calendar synchronization.
Voice Interface
Voice-to-text transcription and reminder deletion through the delete_reminder MCP tool.
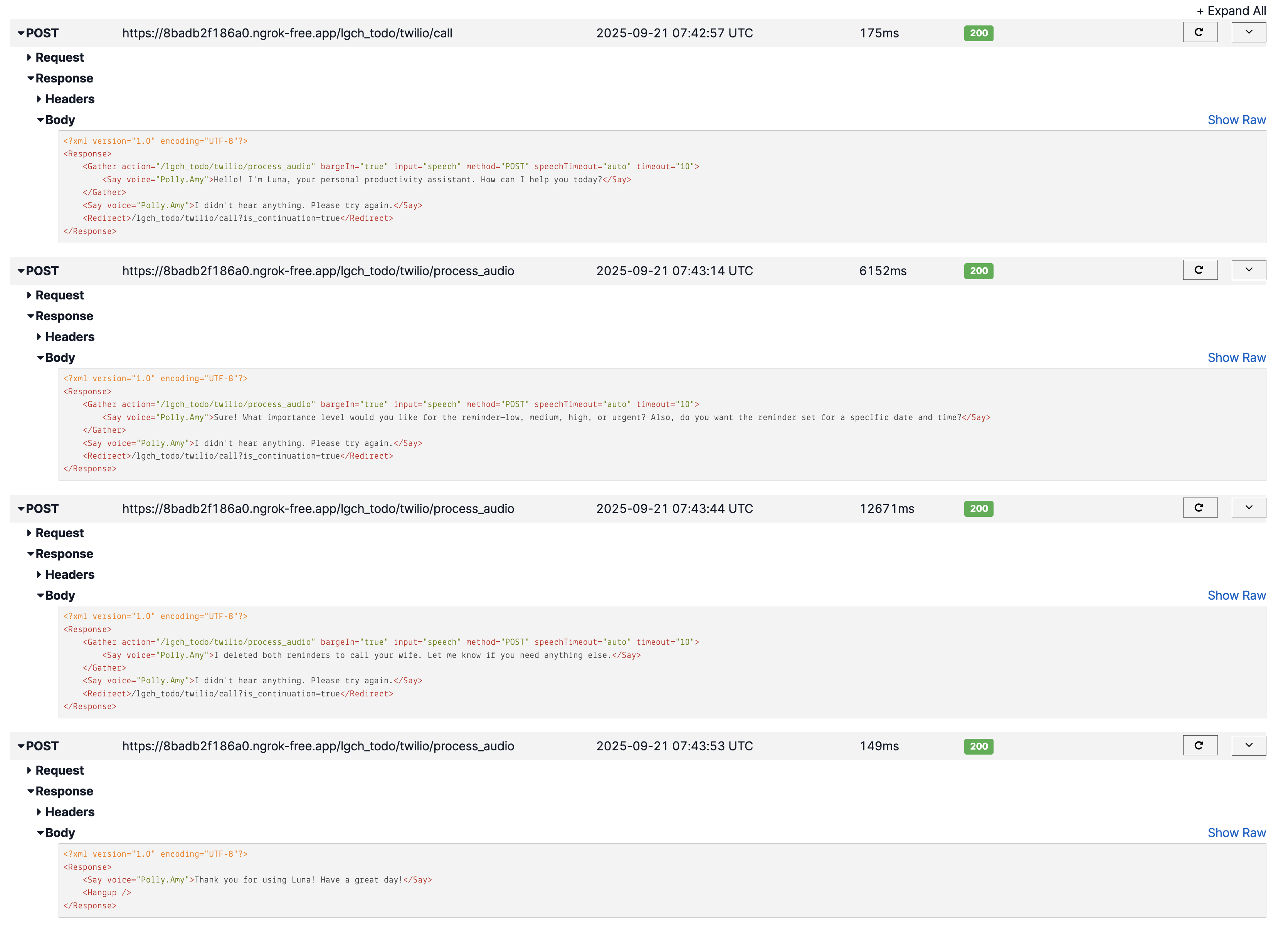
Audio: "Delete the reminder to call my wife"
Output: ✅ Reminder deleted via voice
Database Removal
delete_reminder MCP tool successfully removes reminders from PostgreSQL database.
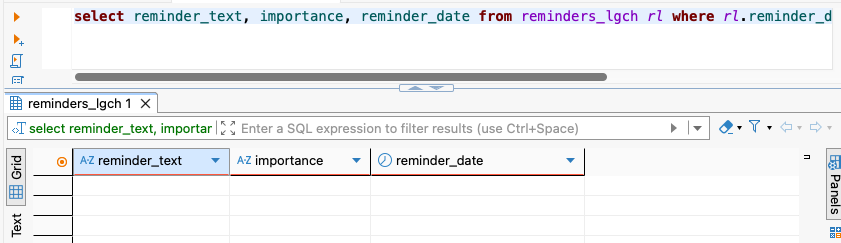
Result: ✅ Reminder removed from DB
Calendar Synchronization
delete_reminder tool automatically removes corresponding Google Calendar events.
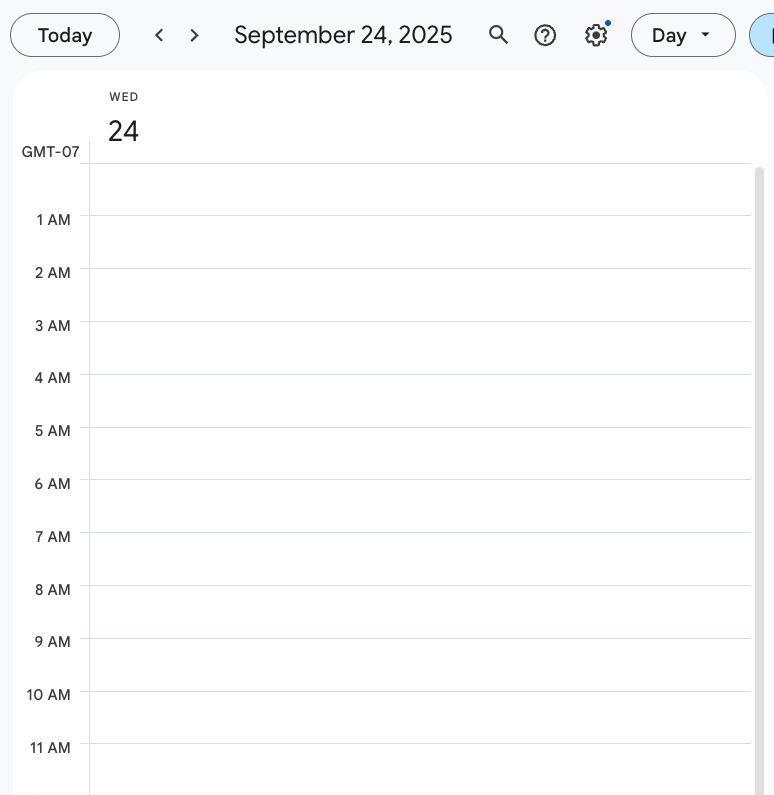
Result: ✅ Event removed from Google Calendar
✅ MCP Tools - Complete Integration Test
1. create_todo Tool Components
- ✅ Voice Input Processing (Twilio Media Streams)
- ✅ Speech-to-Text (OpenAI Whisper)
- ✅ MCP Tool Execution (create_todo function)
- ✅ Database Storage (PostgreSQL)
- ✅ Calendar Sync (Google Calendar API)
2. complete_todo Tool Components
- ✅ Voice Input Processing (Twilio Media Streams)
- ✅ Speech-to-Text (OpenAI Whisper)
- ✅ MCP Tool Execution (complete_todo function)
- ✅ Database Update (PostgreSQL)
- ✅ Calendar Update (Google Calendar API)
3. create_reminder Tool Components
- ✅ Voice Input Processing (Twilio Media Streams)
- ✅ Speech-to-Text (OpenAI Whisper)
- ✅ MCP Tool Execution (create_reminder function)
- ✅ Database Storage (PostgreSQL)
- ✅ Calendar Sync (Google Calendar API)
4. delete_reminder Tool Components
- ✅ Voice Input Processing (Twilio Media Streams)
- ✅ Speech-to-Text (OpenAI Whisper)
- ✅ MCP Tool Execution (delete_reminder function)
- ✅ Database Removal (PostgreSQL)
- ✅ Calendar Sync (Google Calendar API)
create_todo Flow: Voice Input → Speech-to-Text → LangGraph Agent → create_todo MCP Tool → Database Storage → Google Calendar Sync → Text-to-Speech Response
complete_todo Flow: Voice Input → Speech-to-Text → LangGraph Agent → complete_todo MCP Tool → Database Update → Google Calendar Update → Text-to-Speech Response
create_reminder Flow: Voice Input → Speech-to-Text → LangGraph Agent → create_reminder MCP Tool → Database Storage → Google Calendar Sync → Text-to-Speech Response
delete_reminder Flow: Voice Input → Speech-to-Text → LangGraph Agent → delete_reminder MCP Tool → Database Removal → Google Calendar Removal → Text-to-Speech Response
Supporting Infrastructure
- ✅ LangGraph Agent Processing
- ✅ Text-to-Speech (OpenAI TTS)
- ✅ Call Recording System
- ✅ WebSocket Communication
- ✅ ngrok Tunnel Management
- ✅ MCP Server Integration